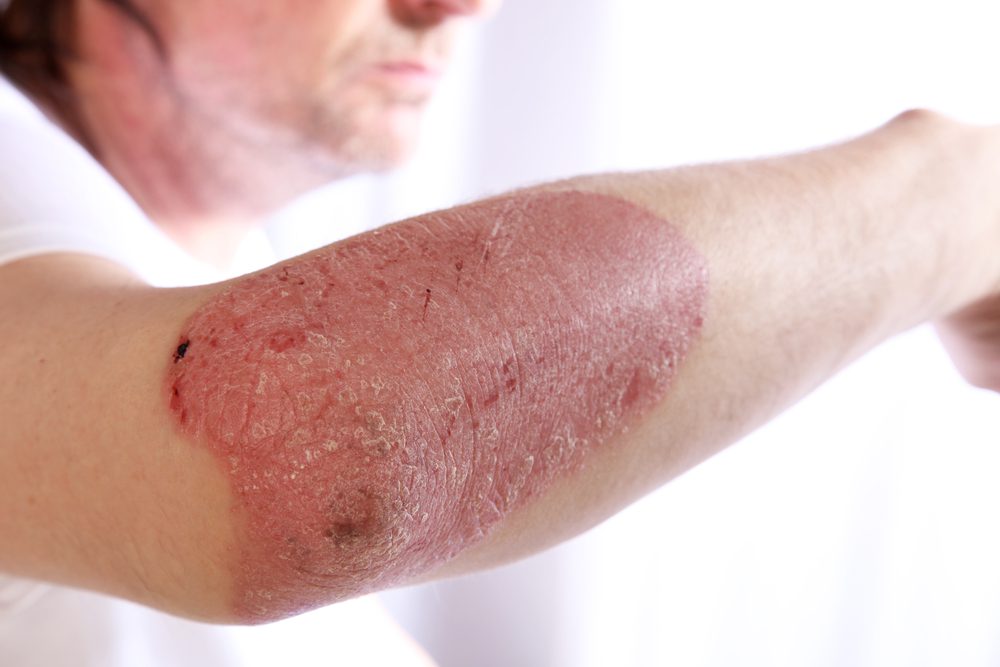
Plaque Psoriasis is the most common type of Psoriasis and causes scaly skin patches that are dry and itchy.
These patches typically appear on the scalp, lower back, knees or elbows. While these patches should be treated immediately, they are not contagious.
What Are The Most Common Types of Plaque Psoriasis?
- Small Plaque Psoriasis
- Large Plaque Psoriasis
- Unstable Plaque Psoriasis
- Chronic Plaque Psoriasis
While the small and large versions are self-explanatory, unstable Plaque Psoriasis lose their edges, often blending together or appearing in new spots. The chronic version tends to appear on both sides of the body, sticking around or reappearing after their first outbreak.
What Causes/Triggers Plaque Psoriasis?
While the medical community isn’t sure how people get Plaque Psoriasis, the most common causes or triggers of Plaque Psoriasis can include the following:
- Heredity
- Infections
- Skin injuries
- Specific medications, and starting or stopping medications
- Stress
- Tobacco use
- Alcohol consumption
What Are The Symptoms of Plaque Psoriasis?
Common symptoms can include:
- Cracked skin that may bleed
- Dry, itchy, burning, sore skin
- Patchy rashes
- Rashes with varying colors
- Small scaling spots
- Rashes that appear for a few weeks/months, then disappear
What Treatments Are Available for Plaque Psoriasis?
While there is currently isn’t a cure, Plaque Psoriasis, it can be treated in the following ways.
- Light Therapy
- Topical Medications
- Biologic Drugs
- Systemic Drugs
Light therapy is used for widespread rashes and involves treatments with ultraviolet light. Topical treatments are typically used for small outbreaks of Plaque Psoriasis and applied directly to the skin.
Systemic drugs are used for severe cases and are designed to work in the entire body, calming the immune system. They must be used with care as they can cause problematic side effects. A type of systemic drug, biologic drugs are designed to work with the immune system and prevent inflammation.







