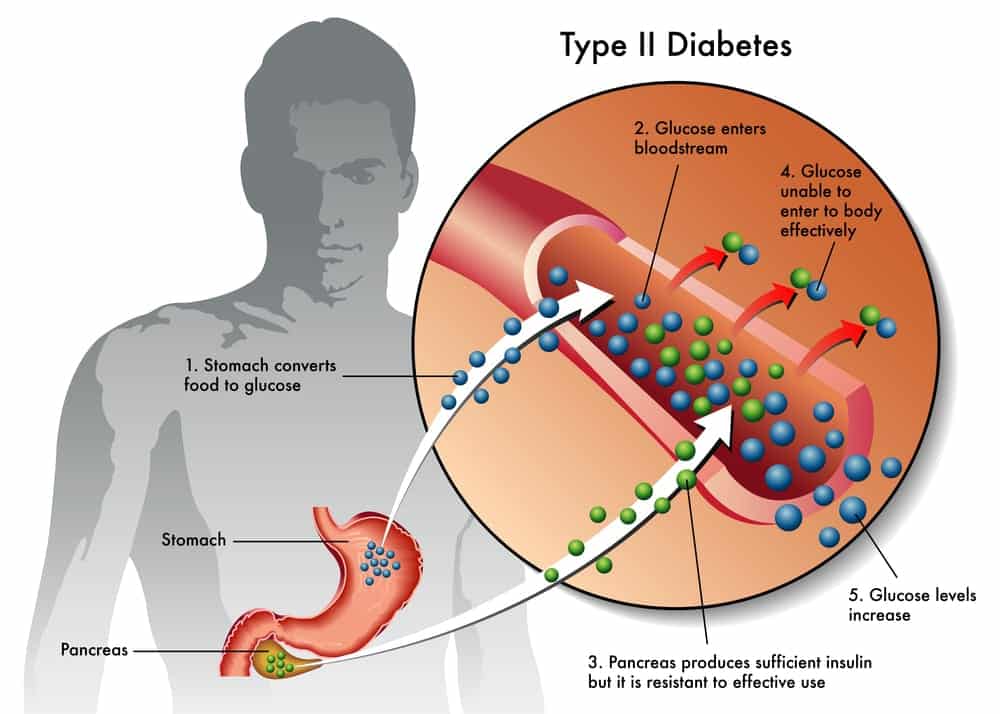
The most common form of diabetes – type 2 diabetes occurs when your body doesn’t use insulin properly.
There are 6 core type 2 diabetes treatments:
- Blood Sugar Monitoring
- Healthy Eating
- Weight Loss
- Exercise
- Diabetes Medications
- Insulin Therapy
All of the treatment management options above are designed to keep your blood sugar levels close to normal, delaying or preventing issues down the road.
Blood sugar monitoring will vary from occasional tests to several times a day if someone is on insulin. There are several tools available for this and it’s the only way to make sure blood sugar levels are where they should be.
Healthy eating can be hugely impactful for those suffering from type 2 diabetes. There is no specific diet, e.g., Atkins, for diabetes. Rather following guidelines that include reducing calories, carbohydrates and saturated fats, while focusing on more fiber based foods, including vegetables and fruits.
Consulting a registered dietitian can help follow these specific guidelines and help develop a plan that works for anyone.
Studies indicate that losing just 5 to 10 percent of your body weight can make a difference in your blood sugar levels, with a sustained weight loss of at least 7 percent to be effective long term.
While diet can help with body weight, exercise is also a key player in type 2 diabetes treatments.
30 to 60 minutes of moderate exercise a day during the week. Simple activities like walking, dancing, swimming, biking – can all have a huge impact on your health.
Anyone starting this as a form of diabetes treatment should consult their doctor before starting, especially those taking diabetes medications as exercise can lower blood sugar levels.
Types 2 Diabetes Medications Can Include
- Metformin – often the first medication prescribed with type 2 diabetes, it lowers glucose production in the liver so the body uses insulin more effectively.
- SGLT2 inhibitors – prevents the kidneys from reabsorbing sugar into the blood.
- Sulfonylureas – allows the body to secrete more insulin.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists – injectable medication, slows digestion, lowering blood sugar levels.
- Meglitinides – quickly stimulate the pancreas to secrete more insulin.
- DPP-4 inhibitors – can help reduce blood sugar levels.
- Thiazolidinediones – cause the bodies tissues to be more sensitive to insulin.
In addition, insulin therapy requires insulin shots, which can be a mixture of insulins designed to work day and night.
Insulin must be given by shots since normal digestion prohibits insulin taken by mouth.
Finally, individuals with a BMI greater than 35 may be eligible for bariatric surgery. Designed for weight loss, it can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar levels.
All of the type 2 diabetes treatment options above should be part of a plan designed by a doctor as there is no one size fits all treatment plan for type 2 diabetes.